Standard drill pipe is the main component of the drill string. It is connected to the square drill pipe at the top and the drill collar at the bottom. It transmits torque to push the bit down and deepen the hole. Drill pipe threads and connectors are an important component of a drilling rig, they play a crucial role in transferring drilling torque to the drill bit. The drill pipe is also prone to bending, pulling, and torsion, the proper drill pipe threads undergo a comprehensive inspection process to ensure its optimum performance. When it comes to drill pipe connection threads, there are a variety of options that you can choose from. There are a number of different drill pipe connection threads that you can choose from. It can be confusing, but if you follow a few simple rules, you can get the one that works for your drill and your job.
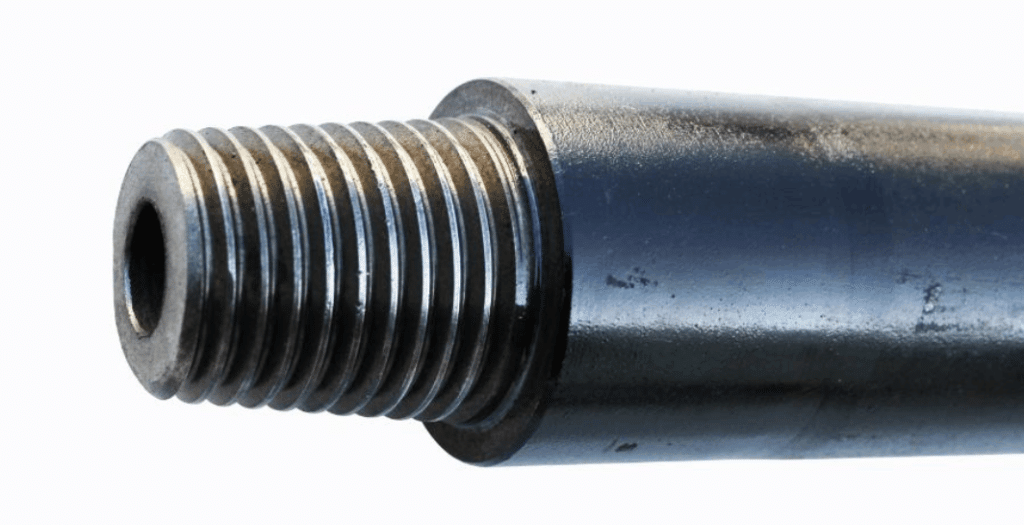
The American Petroleum Institute’s Committee on Drilling Service Equipment decided in 1968 to adopt 11 of the 13 sizes of joints in this series as the official standard. Two digits indicate the pitch circle diameter of the male buckle base thread, that is, the number type joint — NC (such as: NC26, NC31, NC38, NC40, NC46, NC50). The NC joint is a V-thread with a V-0.065 “flat top and a 0.038” circular bottom. It is expressed in V-0.038R and can be connected to V-0.065.
NC26 is the full-hole connection, which is ideal for an internal upset drill pipe. The outer diameter is slightly smaller than the diameter of the thickened portion of the pipe, making it a simple design to assemble and it makes a nice addition to the drilling suite. Drill pipe has a number of different requirements that must be met to meet its operational specifications, including NC38, NC40, CN46, and NC50. This includes the ability to withstand torsion, bending, and external pressure. It also must be able to transfer torque to the drill bit. In addition to these, it must be capable of handling a wide range of rig motions.
Internal-flush(IF) connection threads
IF style joint thread is connected to the drill pipe with external or internal thickening, the inner diameter of the drill pipe joint and the inner diameter of the pipe body is equal to or similar to the diameter of the pipe body. The drilling fluid flow resistance is low, but the outer diameter is large and easy to wear. V-0.065 flat top flat triangle teeth are used for all specifications of threads. This form type has a flat base and a top width of 0.065 inches (1.651mm) except for 5 1/2 IF, threads of other specifications are substituted because their structural dimensions are identical to those of the corresponding NC type. However, this thread has been eliminated by the API due to the stress concentration caused by its form structure, including 4 1/2 IF and 4 IF, that replaced by NC50 and NC46 threads.
Full hole(FH) connection thread
The full hole(FH) drill pipe joint thread connects the inside and outside of the thickened drill pipe so that the inside diameter of the drill pipe joint is equal to the thickened end and less than the inside diameter of the drill pipe. The thread specifications are small in number, using V-0.065, V-0.050 (arc base, 0.050 inches, 1.27mm) and V-0.040 (arc base, 0.040 inches, 1.02mm). They have been widely used in square-tooth drill pipes, drill collars, and drill bits. Now, except for 5 1/2 FH and 6 5/8 FH, which use V-0.050 teeth and 1:6 taper, the rest are eliminated by API. The only 4 FH thread using V-0.065 was replaced by the number style NC40 thread as well as the internal flat thread.
Regular style connection thread
Regular(RGE) style drill pipe threads are usually used, is quite common in oilfield practices. They offer a decidedly lackluster torsional strength. The REG drill pipe joint thread was used to connect the internal thickened drill pipe so that the inside diameter of the drill pipe joint was less than the inside diameter, and the inside diameter of the thickened end of the drill pipe was less than the inside diameter. API designed regular threads primarily for use in bit connections. Since the bit is located at the end of the drill string, where the presence of stress concentration at the bottom of the thread is irrelevant, API has kept them to all specifications. This model uses V-0.050 and V-0.040 teeth. The API SPEC 7 40th Edition has added 1REG and 1 1/2 REG threads using V-0.055 (flat base, 0.055 inch, 1.397mm) teeth.






