As we know, according to the content of alloy elements in steel, it can be divided into carbon steel and alloy steel. High carbon steel, often referred to as tool steel, is the steel with a carbon content from 0.60% to 1.70%, mainly used for cutting tools manufacturing. Manganese steel, also known as manganese alloy steel, is a kind of high-strength steel. While they’re both tough and durable, they have different properties. This article will compare high carbon steel and high manganese steel.
As their name implies, the difference between high carbon steel and high manganese steel is also regarded as the difference between carbon steel and manganese steel. We usually consider steels with a carbon content of less than 2.11% without special alloying elements. Sometimes called plain carbon steel or carbon steel. It also contains small amounts of silicon, manganese, sulfur and phosphorus.
Manganese steel is a high-strength steel that typically contains 11 to 14 percent manganese. It is typical wear-resistant steel with austenite and carbide as cast structure. After water quenching at about 1000°C, the microstructure changed into a single Austenite or Austenite with a small amount of carbide. Manganese steel is mainly used for where withstand strong impact, deformation, extrusion, wear and other harsh conditions.
Hardness
We know carbon is the basic element of steel, manganese steel may also contain 1.0%~1.3% of carbon. When compared to high carbon steel, manganese steel is harder. High carbon steels gain strength through tempering, while manganese steel is softer and less abrasion resistant. Carbon steels are typically stronger than manganese steel, but it’s possible to create an alloy with a lower manganese content.
In general, the higher the carbon content of carbon steel, the higher the hardness and strength, the lower the plasticity. High carbon steel has higher hardness and toughness than high manganese steel (spring steel), under the same strong impact of high carbon steel is very likely to fracture. For example, the strength, hardness, elasticity and hardenability of 65Mn steel plate are higher than AISI 1065 steel, with overheating sensitivity and temper brittleness tendency, water quenching has a tendency to form cracks.
Wear resistance
The most important feature of high manganese steel is that under strong impact and extrusion conditions, its surface rapidly hardening and the core still maintain good toughness and plasticity of Austenite, which makes it have good wear resistance, which is better than other materials. But the wear resistance of high manganese steel shows its superiority only under the condition of sufficient work hardening.
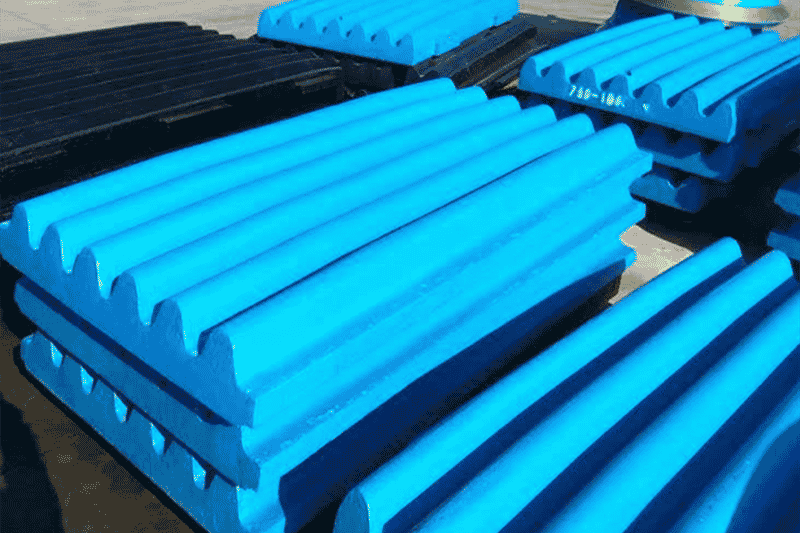 Applications
Applications
In short, high carbon steel is more corrosion resistant, while low manganese steel is prone to wear and tear. High carbon steel often called tool steel is mainly used in CNC machining cutting tools. Drills, taps, reamers and other tools are made from 0.90% to 1.00% carbon steel. It is characterized by hardness and brittleness. High carbon steel is better for structural applications, such as in heavy-duty parts. For example, AISI 1095 is a type of high carbon steel with high hardness and wear resistance, it’s often used for knives and daggers.
Manganese steel is also less brittle than carbon steel. Manganese steel can be forged into intricate shapes, such as circles, which gives them a unique appearance. Aside from the strength and durability of these steels, they have other properties that make them desirable for industrial applications. As a typical wear-resistant steel, high manganese steel is mainly used to withstand impact, extrusion, wear and other harsh conditions, is an excellent material for crusher parts manufacturers. In addition, wear-resistant high manganese steel is also suitable for impact and high stress grinding abrasive wear conditions, often used to manufacture ball mill lining plates, hammer crusher hammer, jaw crusher jaw plates, cone crusher mortar walls, broken walls, excavator buckets, railway turnout, tractor and tank track plate casting.
In the last
There are advantages and disadvantages to both high carbon steel and high manganese steel. If you’re looking for good steel for your projects, it depends on what you’re using it for, that is, the balance of carbon and manganese elements. While carbon steels are cheaper to manufacture and use, they still show a significant amount of degradation when exposed to hydrogen. Although carbon-manganese steels are harder than common structural steels, they have a much lower yield strength and less ductility. Therefore, if you’re looking for very strong steel, you may want to consider carbon-manganese steel. It’s a great choice for a wide range of applications and is also cheaper to produce than manganese steel.






