Chromoly steel is a medium carbon, low alloy, medium temperature hydrogen resistant steel with alloying elements such as chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), iron (Fe) and carbon (C), the elements chromium and molybdenum contribute to its high tensile strength and toughness. It has good quenching properties and can be deeply quenched, and its ability to be heat-treated for improved strength and hardness makes it ideal for applications requiring resistance to fatigue and stress.
4130 is one of the commonly used chromoly steel, it is a type of alloy steel known for its exceptional strength, durability, and weldability. and is commonly used in various applications such as high-temperature and high-pressure resistant vehicles, automotive parts, aerospace components, screwdriver heads, bikes and motorcycle frames and structural tubing where lightweight yet strong materials are required. The equivalent materials of 4130 in different standards include:
Grade 4130 ASTM A29
Grade 4130 ASTM A1031
UNS G41300
SCM430 JIS G4105
34CrMo4 DIN EN 10083-3 1.7220
30CrMo GB/T 3077-2015
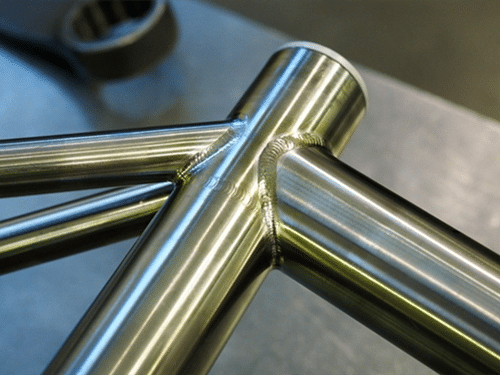
As a welding engineer, 4130 chromoly steel is favored in industries where a combination of strength, ductility, and affordability is crucial. Its excellent weldability also makes it suitable for fabrication processes, including welding, brazing, and machining. Additionally, its relatively low carbon content compared to other types of steel helps to maintain its weldability while still providing excellent mechanical properties. The following are the most common 10 problems of 4130 chromoly steel material welding with argon arc welding. It is mainly for the field of sports, such as aircraft samples, racing frames, anti-roll frames, sand bikes, bicycle and motorcycle racks, etc., which should be re-considered according to the specific use.
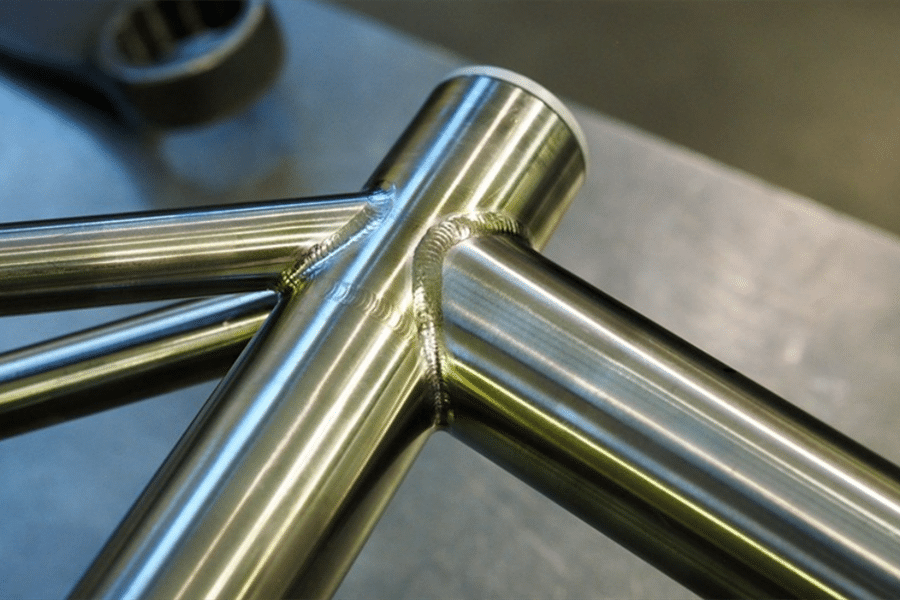
A: Yes, the practice of argon arc welding 4130 chrome-molybdenum material has been used in the aerospace field for many years. Like all welding, argon arc welding needs to follow reasonable steps and methods.
Q: Do I need to pre-heat?
A: Parts of thin-walled tubes (less than 0.12 “or 3mm thick) generally do not require preheating of 300-400 F (about 149-204 C) to achieve the desired effect. However, the temperature of the steel pipe itself should not be lower than 70 degrees Fahrenheit (about 21 degrees Celsius) at room temperature before welding.
Q: What kind of wire should I use?
A: Although there are many choices of welding wires available, none more so than the ER80S-D2. The weld strength of this electrode is basically close to the strength of 4130 material itself. ER70S-2 can also be considered, but its weld strength is slightly weaker.
Q: With ER70S-2 welding wire, does it sacrifice strength and gain better ductility?
A: Yes, when the welding wire and the base material fuse, the strength of the welding wire is generally less than the strength of 4130. However, through reasonable structural design (such as adding stiffeners or support pipes), multi-point supports and longer welds can make up for the lack of strength of the welding wire itself.
Q: Why not recommend 4130 material welding wire?
A: The welding wire of 4130 is generally used on the workpiece that will be heat-treated in the later stage. Because of its high hardness and insufficient ductility, it is not recommended for use on sports equipment, such as aircraft, racing frames and tumbling frames.
Q: Can I use other welding wires for 4130?
A: Some welding engineers like to use austenitic stainless steel wire to weld 4130 steel pipes. 310 and 312 grades of stainless steel welding wire are also used, other grades of stainless steel can cause cracking. In addition, stainless steel welding wire is usually more expensive.
Q: Does the workpiece of 4130 need heat treatment to remove stress after welding?
A: Thin-walled pipes generally do not need to stress, the wall thickness of more than 0.12 “or 3mm of the 4130 steel tubing after welding can be heat treatment, the best treatment temperature of the pipe fittings is 1100 degrees Fahrenheit (about 593 degrees Celsius), oxygen and acetylene formed by the neutral flame can be used to heat, the heating process needs to keep moving to avoid local overheating.
Q: Does 4130 material need to be cleaned before welding?
A: Of course. Impurities and oil on the surface of the steel pipe need to be cleaned with medium sandpaper and acetone. Burrs and corner tips need to be polished, and the welding effect will be better when the clean contact surface comes out.
Q: Does the back of 4130 material need gas protection when welding?
A: It is generally not necessary to weld the back gas protection, although some welders do this, the back gas protection is not harmful to welding, and will improve the weld quality of the weld bead for some welding.
Q: Can the welded 4130 tubes be quenched?
A: No, rapid hardening of welding parts will cause a lot of problems, such as cracks or delamination tearing, it is best to cool naturally.
Rapid link: How to weld ASTM A519 Gr.4130 steel tubing