The sucker rod is a crucial component of rod pumping equipment. It connects the upper rod to the pumping unit through a coupling. The plunger of the pumping unit is attached to the sucker. The sucker’s function is to transfer the movement of the ground pumping unit to the downhole oil pump. Thread failure is a common problem, resulting in thread pull. A modern API sucker’s thread is made by rolling rather than turning.
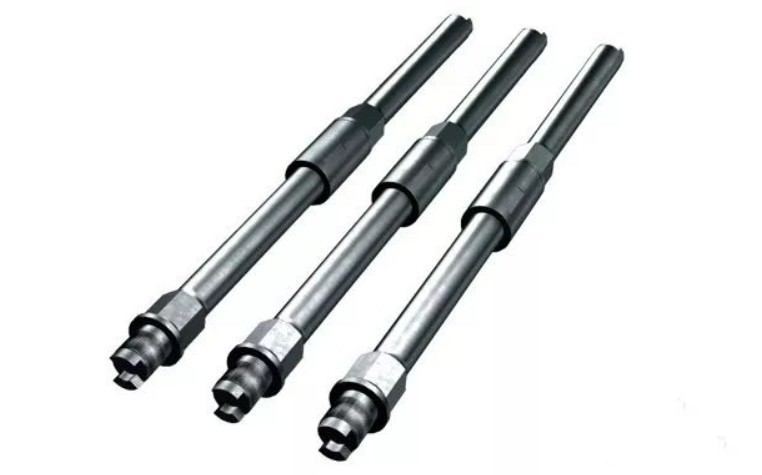 The API Spec. 11B includes specific recommendations and specifications for mechanical properties and operating practices for the steel sucker rods and drive Rod. The API sucker rods have The standard covers general and fiber-strengthened plastic sucker rods, plugging-type and taper thread suckers, and sinker bar. It also specifies testing methods and recommended practices for a variety of rod types, it also includes specific requirements for thread ring, polished rod, and API sucker rod thread plug gages. This standard helps you to ensure that the quality of the finished product meets the required standards. For example, the rod string’s length is not less than the rod’s width and thickness. This means that the sucker-rod string will have the appropriate size. In addition, the API specification requires the materials for the steel drive rods.
The API Spec. 11B includes specific recommendations and specifications for mechanical properties and operating practices for the steel sucker rods and drive Rod. The API sucker rods have The standard covers general and fiber-strengthened plastic sucker rods, plugging-type and taper thread suckers, and sinker bar. It also specifies testing methods and recommended practices for a variety of rod types, it also includes specific requirements for thread ring, polished rod, and API sucker rod thread plug gages. This standard helps you to ensure that the quality of the finished product meets the required standards. For example, the rod string’s length is not less than the rod’s width and thickness. This means that the sucker-rod string will have the appropriate size. In addition, the API specification requires the materials for the steel drive rods.
API 11B classifies common steel sucker rods into four grades: C, D, K and H. Common sucker rod has the advantages of simple production, low cost, small diameter and wide application range, and its utilization rate accounts for more than 90% of sucker rod pumping Wells. The rods are 7.62 or 8 m,9.14m in length. They are usually made of low-carbon alloy steel that has been tempered and tempered. They are connected one by one in the tubing with an internally threaded collar that runs to a piston in the underground reservoir to pump oil by reciprocating motion.
Class C sucker rod: For shallow Wells, light load conditions.
Class D sucker rod: For medium and heavy-duty Wells.
Class K sucker rod: For corrosive light/medium load Wells.
Class K and D sucker rods: Steel sucker rods have the corrosion resistance of class K rods and the mechanical properties of class D rods.
Here, we mainly introduce sucker rods for general use. They are generally carbon steel sucker rods and alloy steel sucker rods. Carbon steel sucker rod is generally made of ANSI 10XX and AISI 15XX high-quality carbon steel; Alloy steel sucker rods are made of AISI 41XX and AISI 46XX steel. Sucker rod breaks easily near the wellhead and thread. Sucker Rods Grade C, D, K steel materials including chemical composition and mechanical properties.
| Grades | Yield strength, Mpa | Steel Types | Steel Material |
| Grades C | 617.4-743.8 | Carbon steel
alloy steel |
4130M |
| Grades D | 793.8-970.2 | Carbon steel
Chromoly steel |
4130M,4320M,4320M,4330M |
| Grade K | 588-793.8 | Ni-Mo steel | 4621M |
Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of steel sucker rods and steel pony rods shall be any composition of AISI series steel, or equivalent, which can be effectively heat treated to the mechanical property requirements of grades K, C, and D rods as shown below
| Grade | Chemical composition |
| K | AISI 46XX series steel |
| C | AISI 10XX series steel
AISI 15XX series steel |
| D Carbon | AISI 10XX series steel
AISI 15XX series steel |
| D Alloy | AISI 41XX series |
| D special | Special alloy shall be any chemical composition that contains a combination of nickel, chromium, and molybdenum that total a minimum of 1.15 % alloying content. |
The endurance limit of steel is determined by a combination of its maximum stress, range of stresses, and a number of stress reversals. In recent years, the harsh working conditions of oil Wells have led to the development of rods made of a variety of materials such as fiber-reinforced (fiberglass) and carbon fiber. Regardless of the material, it is important to select an appropriate one for the job.